835. Image Overlap
You are given two images, img1 and img2, represented as binary, square matrices of size n x n. A binary matrix has only 0s and 1s as values.
We translate one image however we choose by sliding all the 1 bits left, right, up, and/or down any number of units. We then place it on top of the other image. We can then calculate the overlap by counting the number of positions that have a 1 in both images.
Note also that a translation does not include any kind of rotation. Any 1 bits that are translated outside of the matrix borders are erased.
Return the largest possible overlap.
Example 1:
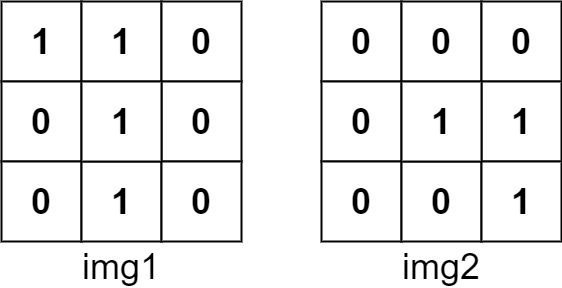
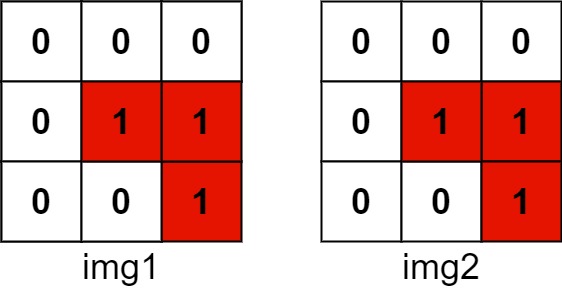
Input: img1 = [[1,1,0],[0,1,0],[0,1,0]], img2 = [[0,0,0],[0,1,1],[0,0,1]] Output: 3 Explanation: We translate img1 to right by 1 unit and down by 1 unit.The number of positions that have a 1 in both images is 3 (shown in red).
Example 2:
Input: img1 = [[1]], img2 = [[1]] Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: img1 = [[0]], img2 = [[0]] Output: 0
Constraints:
n == img1.length == img1[i].lengthn == img2.length == img2[i].length1 <= n <= 30img1[i][j]is either0or1.img2[i][j]is either0or1.
solution:
class Solution {
public:
int largestOverlap(vector<vector<int>>& img1, vector<vector<int>>& img2) {
int n=img1.size();
vector<pair<int,int>>vec_a;
vector<pair<int,int>>vec_b;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(img1[i][j]==1){
vec_a.push_back({i,j});
}
if(img2[i][j]==1){
vec_b.push_back({i,j});
}
}
}
int ans=0;
map<pair<int,int>,int>mp;
for(auto [i1,j1]:vec_a){
for(auto [i2,j2]:vec_b){
mp[{i1-i2,j1-j2}]++;
ans=max(ans,mp[{i1-i2,j1-j2}]);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Comments
Post a Comment