Check if Tree is Isomorphic
Given two Binary Trees. Check whether they are Isomorphic or not.
Note:
Two trees are called isomorphic if one can be obtained from another by a series of flips, i.e. by swapping left and right children of several nodes. Any number of nodes at any level can have their children swapped. Two empty trees are isomorphic.
For example, the following two trees are isomorphic with the following sub-trees flipped: 2 and 3, NULL and 6, 7 and 8.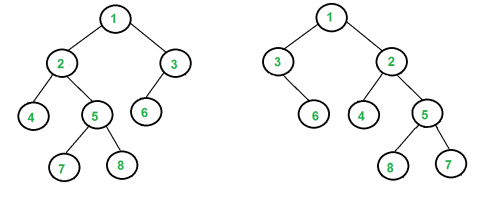
Example 1:
Input:
T1 1 T2: 1
/ \ / \
2 3 3 2
/ /
4 4
Output: No
Example 2:
Input:
T1 1 T2: 1
/ \ / \
2 3 3 2
/ \
4 4
Output: Yes
Your Task:
You don't need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function isomorphic() that takes the root nodes of both the Binary Trees as its input and returns True if the two trees are isomorphic. Else, it returns False. (The driver code will print Yes if the returned values are true, otherwise false.)
Expected Time Complexity: O(min(M, N)) where M and N are the sizes of the two trees.
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(min(H1, H2)) where H1 and H2 are the heights of the two trees.
Constraints:
1<=Number of nodes<=105
solution :
Comments
Post a Comment