Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
Example 1:
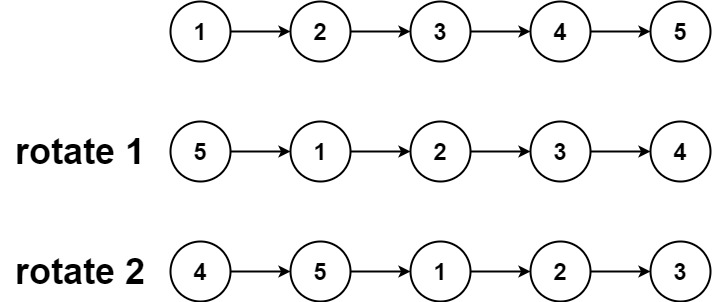
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
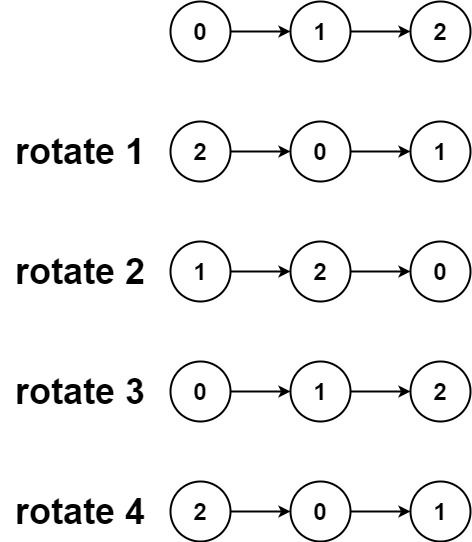
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4 Output: [2,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 500]. -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 109
Solution :
Base Cases: We start by handling the base cases. If the input linked list is empty or has only one element, or if
k is equal to zero, there is no need to perform any rotation, and we return the head as it is.Counting Nodes: We count the total number of nodes in the linked list. This count, stored in
cnt_nodes, is crucial for determining the effective number of rotations.Calculating Effective Rotations: To optimize the rotation, we calculate the effective number of rotations required. This is done by subtracting
(k % cnt_nodes) from the total number of nodes.Performing the Rotation: We then iterate through the linked list, stopping at the node just before the effective rotation point. We update the pointers to achieve the desired rotation, effectively making the new head and breaking the link at the appropriate point.
Returning the Result: Finally, we return the updated
head, which now points to the rotated linked list.
Comments
Post a Comment